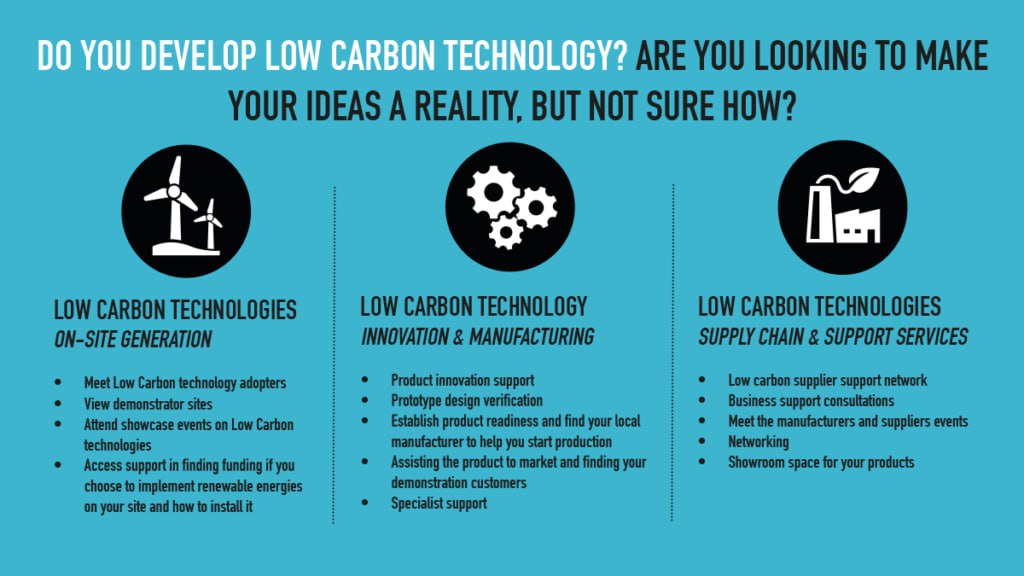
Assistance to Low-Carbon Innovation: Fostering Sustainable Solutions for the Future
With the challenge of climate change growing, low-carbon innovation is critical for a sustainable future. Support for these innovations—whether in energy, transportation, or other sectors—helps overcome challenges and accelerates the global shift to low-carbon economies. This guide examines the importance of assisting low-carbon innovation, types of support available, and how they contribute to climate goals.
What is Low-Carbon Innovation?
Low-carbon innovation involves creating technologies, products, and processes that reduce emissions, enhance energy efficiency, and support sustainability. Examples include renewable energy sources, electric vehicles (EVs), carbon capture, and sustainable agricultural methods. The goal is to minimize environmental impact, foster sustainable growth, and mitigate climate change.
Why is Assistance Needed for Low-Carbon Innovation?
- High Initial Costs: Significant R&D investment is required, which can be prohibitive for startups or businesses in developing regions.
- Risk and Uncertainty: Early-stage technologies face uncertain commercial viability, long timelines, and potential failure, which can discourage investment.
- Lack of Technical Expertise: Innovators often need specialized skills in manufacturing, engineering, and scaling technologies to market.
- Regulatory and Policy Barriers: In many areas, regulations and outdated infrastructure pose challenges to adoption.
- Market Access and Distribution: Reaching consumers and expanding distribution can be challenging, especially in fossil-fuel-dependent regions.
Types of Assistance to Low-Carbon Innovation
1. Financial Support
Grants and Subsidies: Governments and international bodies often fund R&D for low-carbon tech through grants and subsidies, focusing on high-potential early-stage projects.
Venture Capital and Private Investment: Private investors, including venture capitalists and impact investors, provide critical funding to startups in the low-carbon sector, enabling new tech to enter the market.
2. Research and Development (R&D) Support
Public R&D Funding: National governments may allocate funds for R&D in low-carbon technologies to drive innovation and meet climate goals.
Partnerships with Academic Institutions: Collaborations with universities enable innovators to access cutting-edge research and development resources.
3. Technical Assistance and Training
Training Programs: Providing training in new technologies and energy management helps ensure successful adoption and operation of low-carbon solutions.
Consulting Services: Expert consultants assist innovators in overcoming technical challenges and scaling their products.
4. Regulatory and Policy Support
Streamlined Approval Processes: Simplifying regulatory procedures for low-carbon technologies accelerates adoption and market entry.
Incentive Programs: Policies like tax breaks for renewable energy installations and carbon pricing create a favorable environment for low-carbon innovations.
5. Market Access and Awareness Campaigns
Public Awareness Campaigns: Informing consumers about the benefits of low-carbon solutions helps drive adoption.
Market Access Initiatives: Governments can support programs that introduce low-carbon technologies to broader markets and reduce barriers to entry.